In roofing construction, welding techniques are crucial for ensuring a durable and watertight seal. Common roof welding methods include hot air welding, solvent welding, and adhesive bonding (though the latter is not technically welding, it is often categorized similarly in practice). Different welding techniques are suitable for various materials, such as PVC, TPO, and EPDM waterproof membranes. This article provides a detailed explanation of these welding technologies, including their principles, applications, and pros and cons, to help construction teams choose the most suitable method.
Hot Air Welding

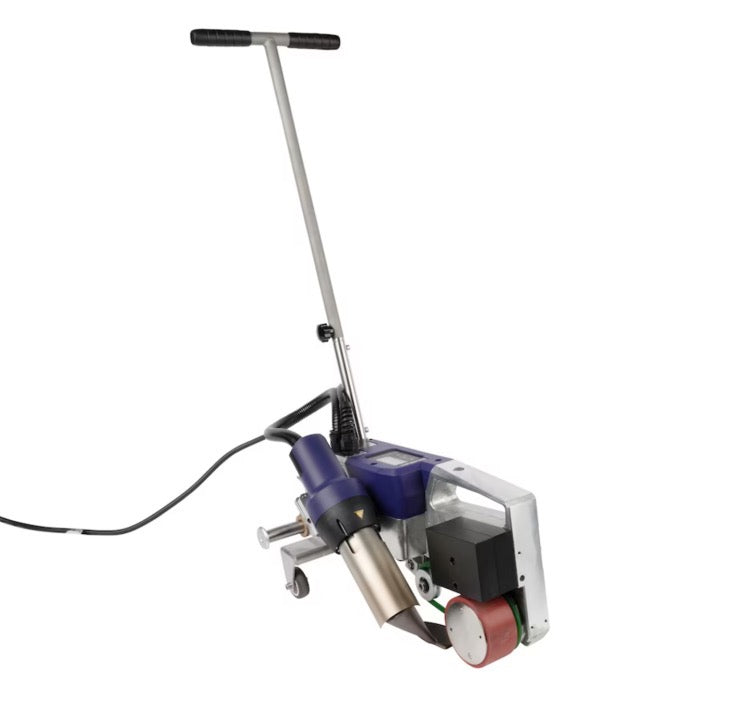
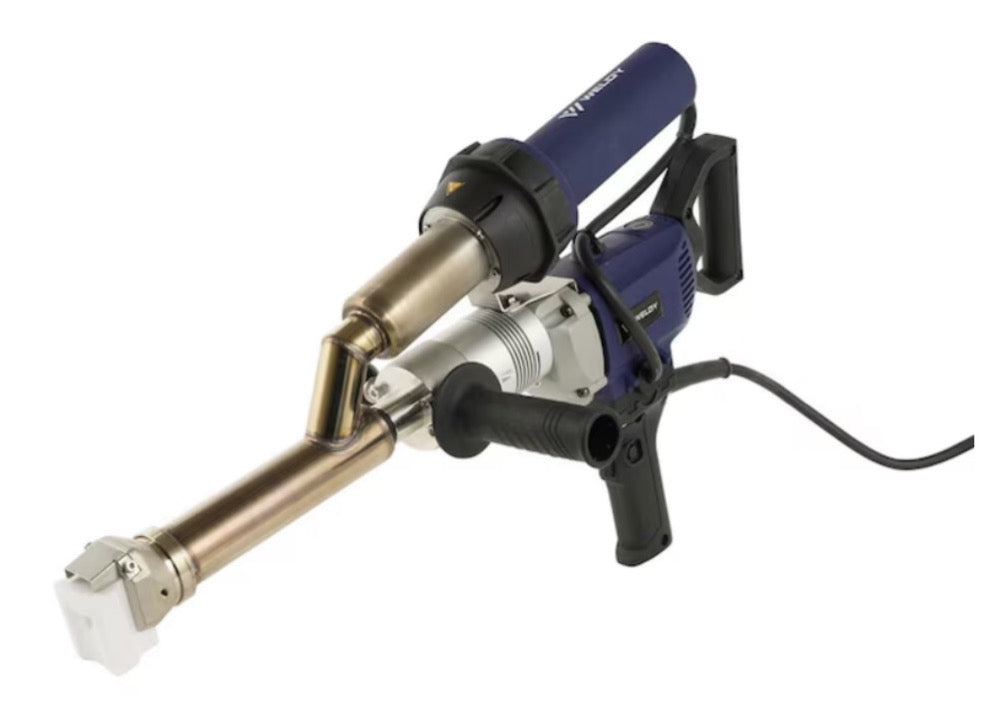
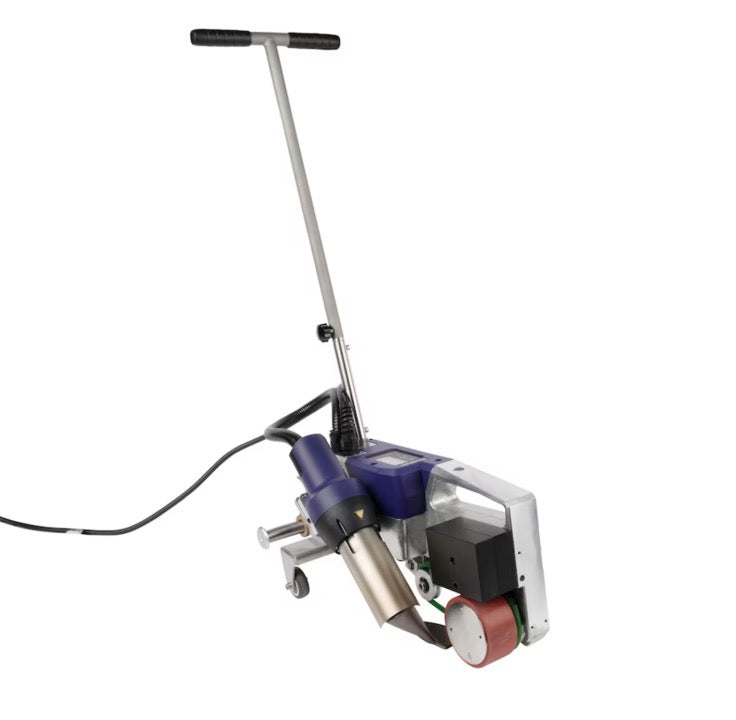
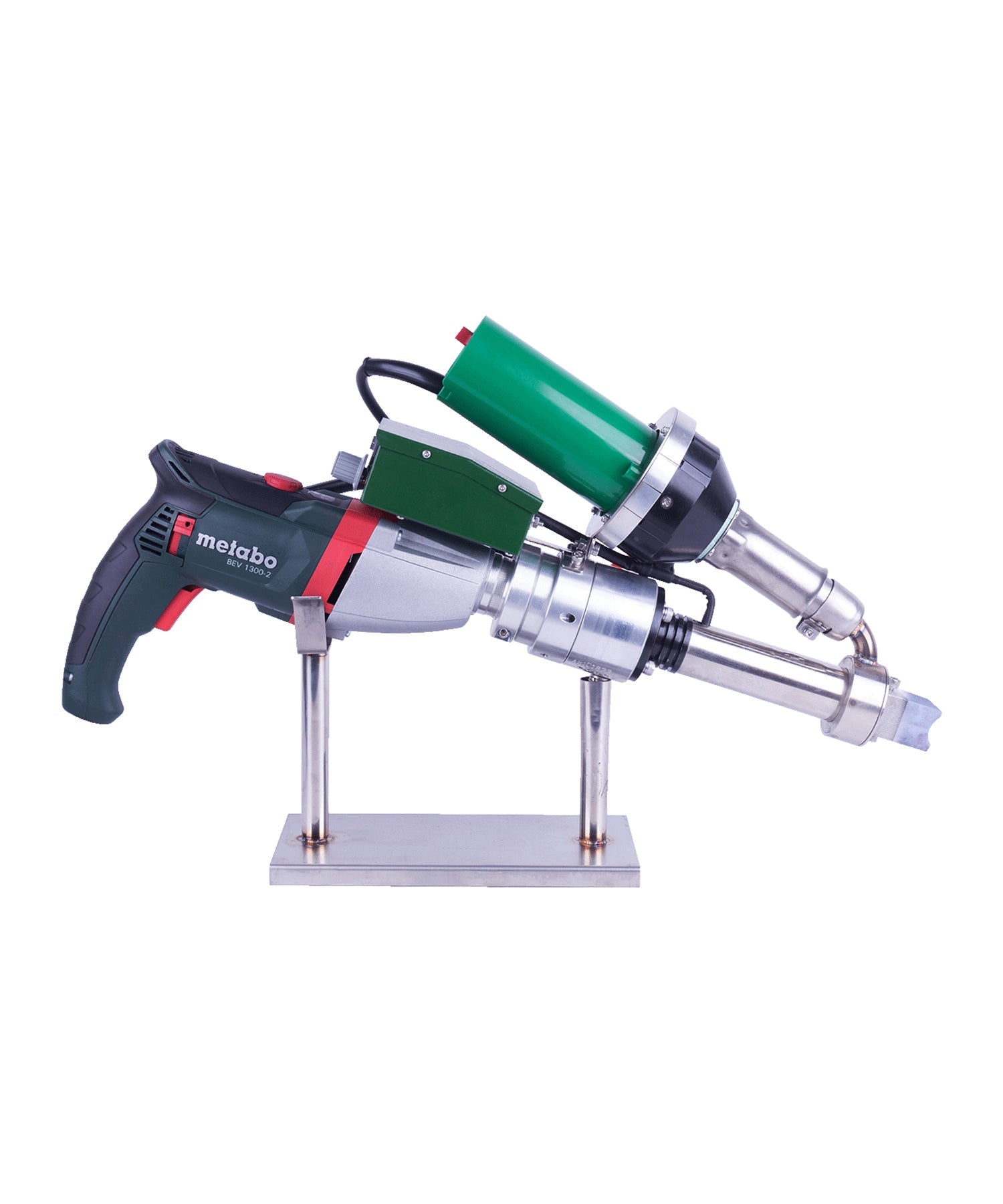
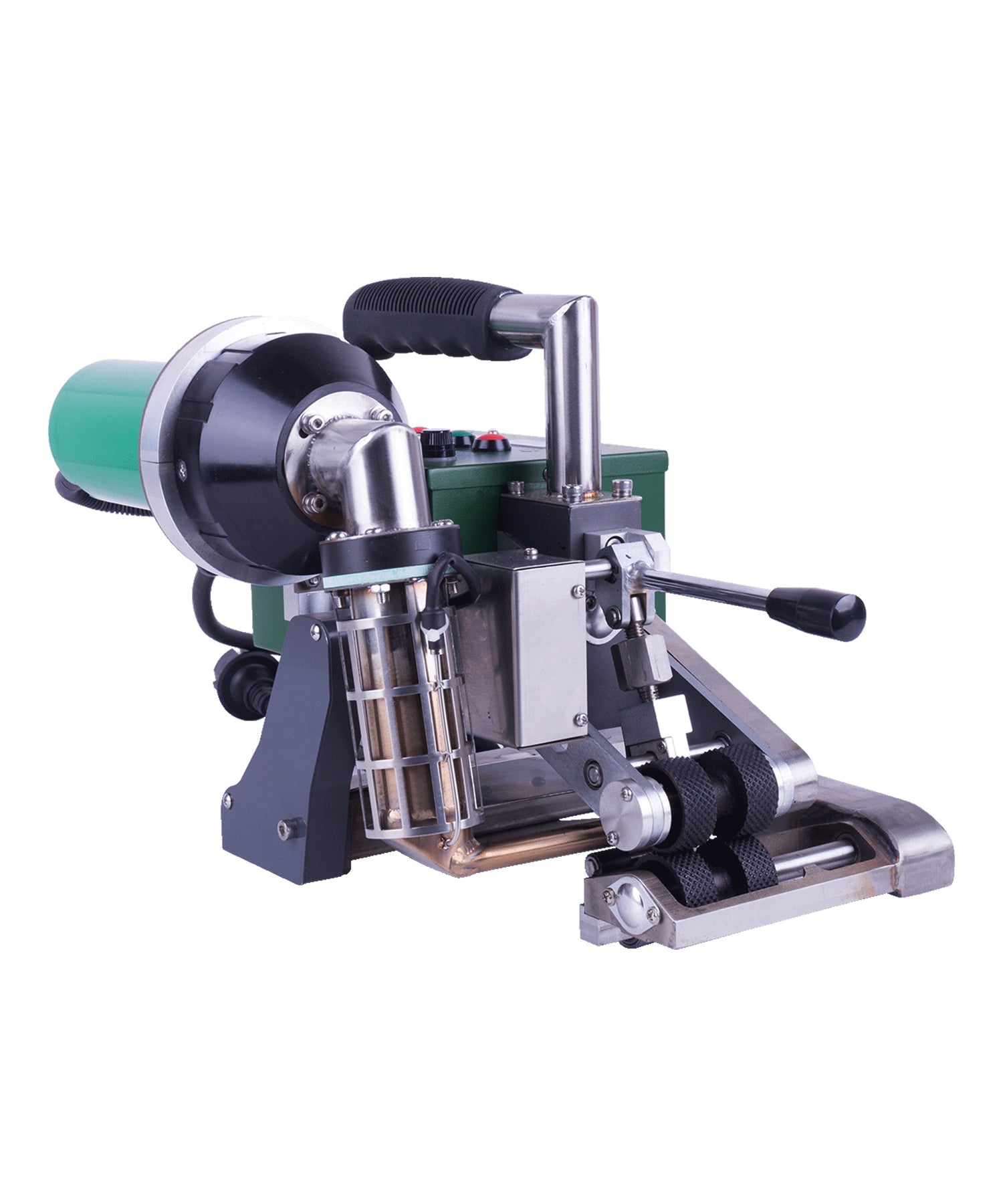
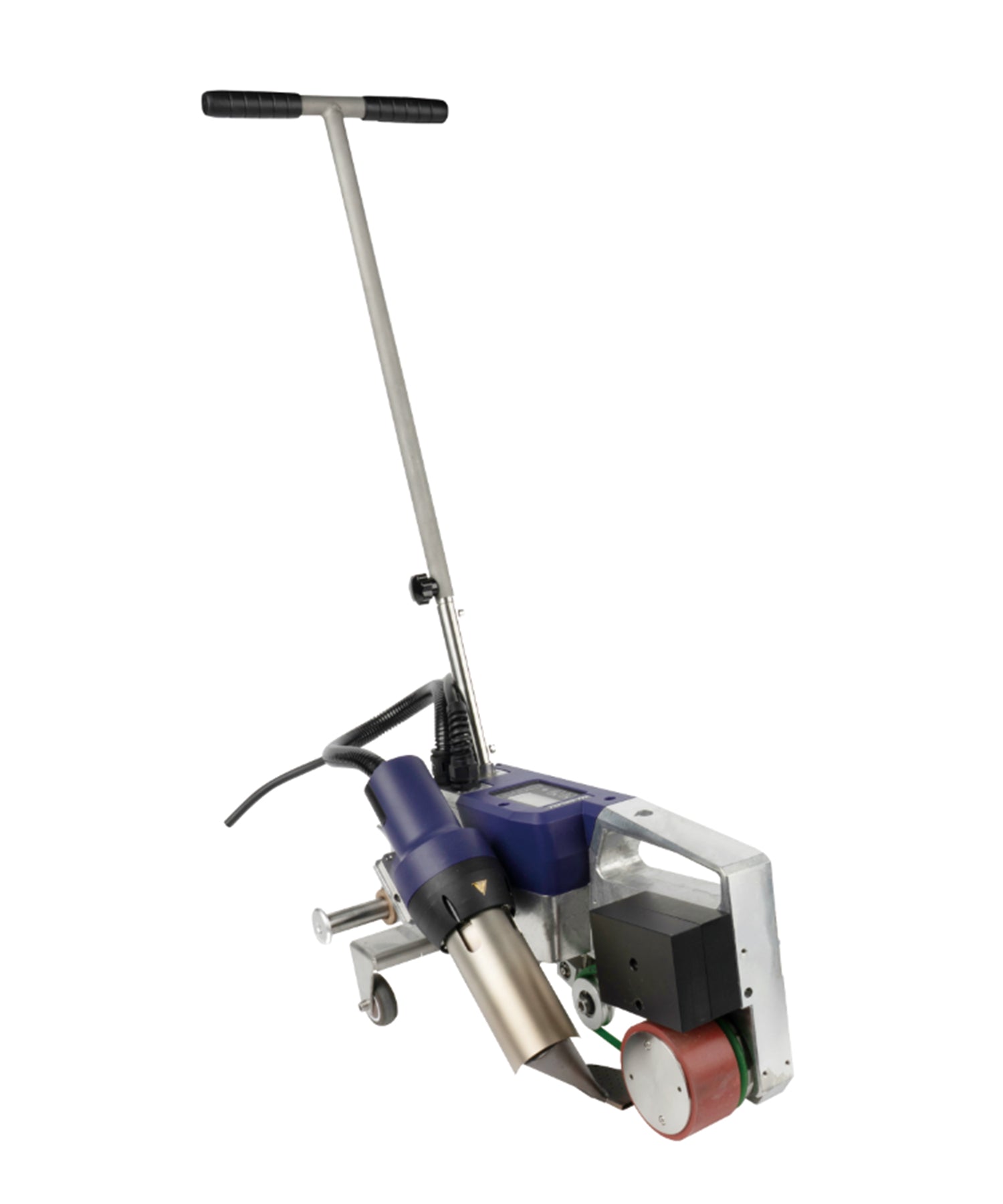
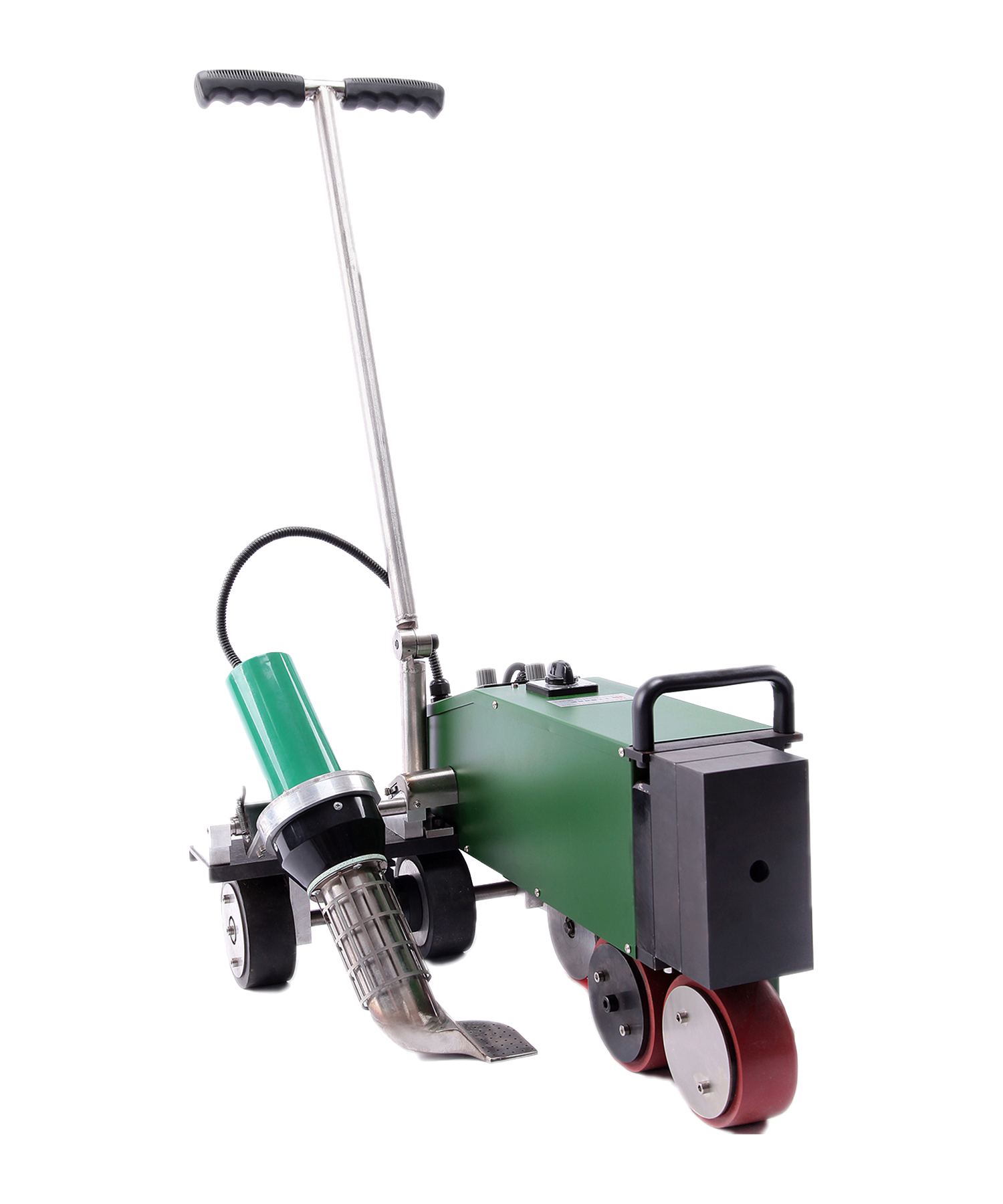
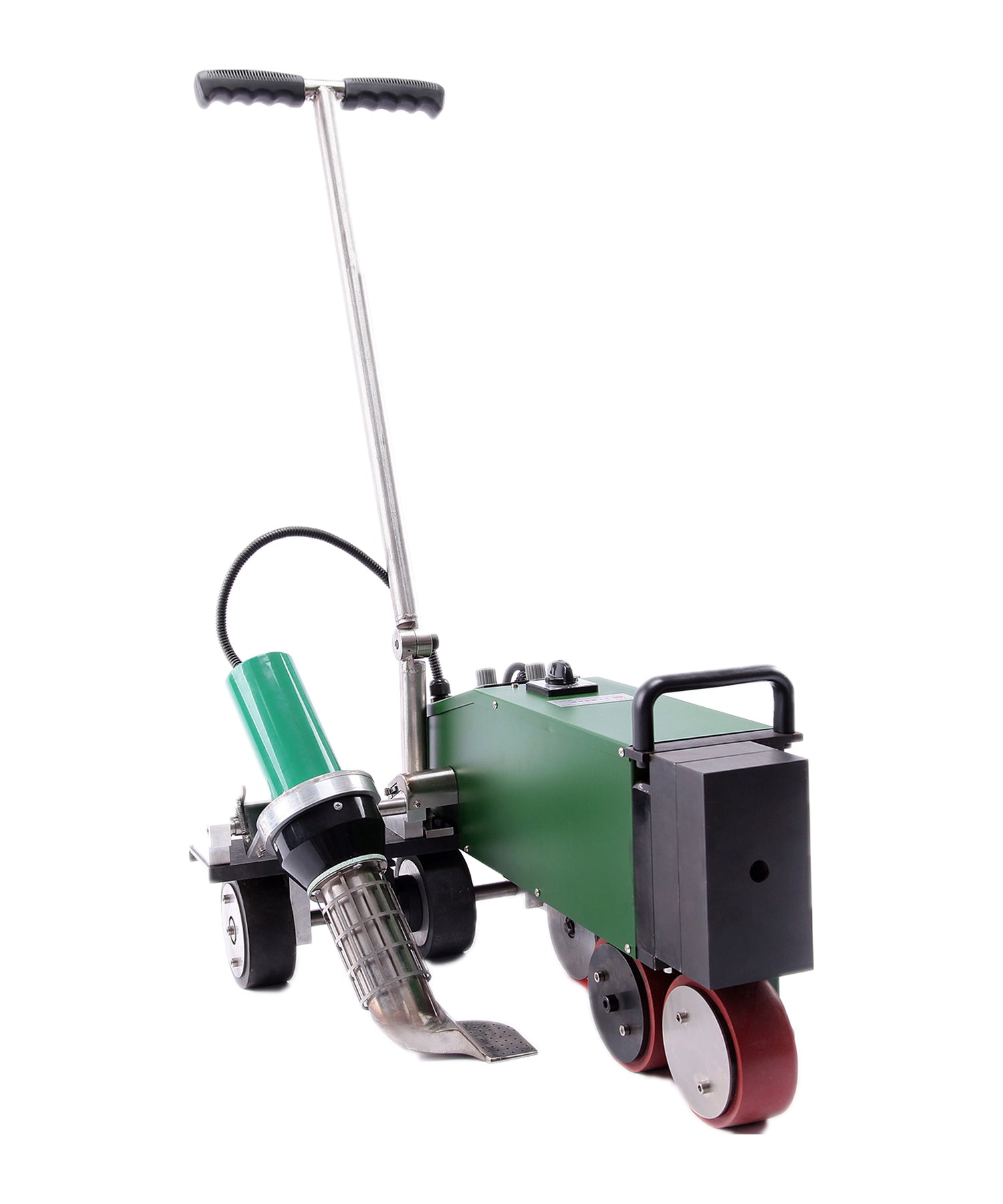
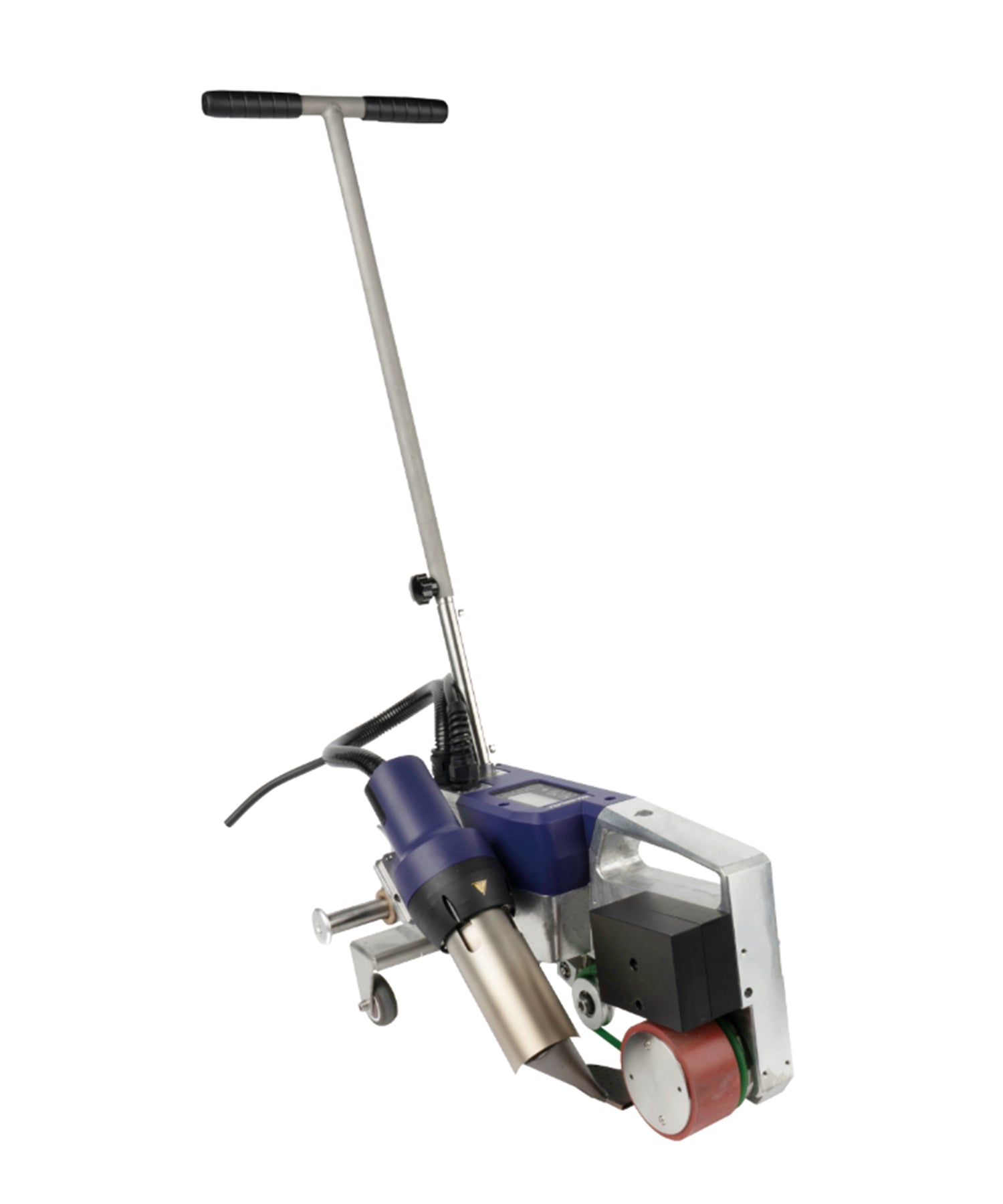
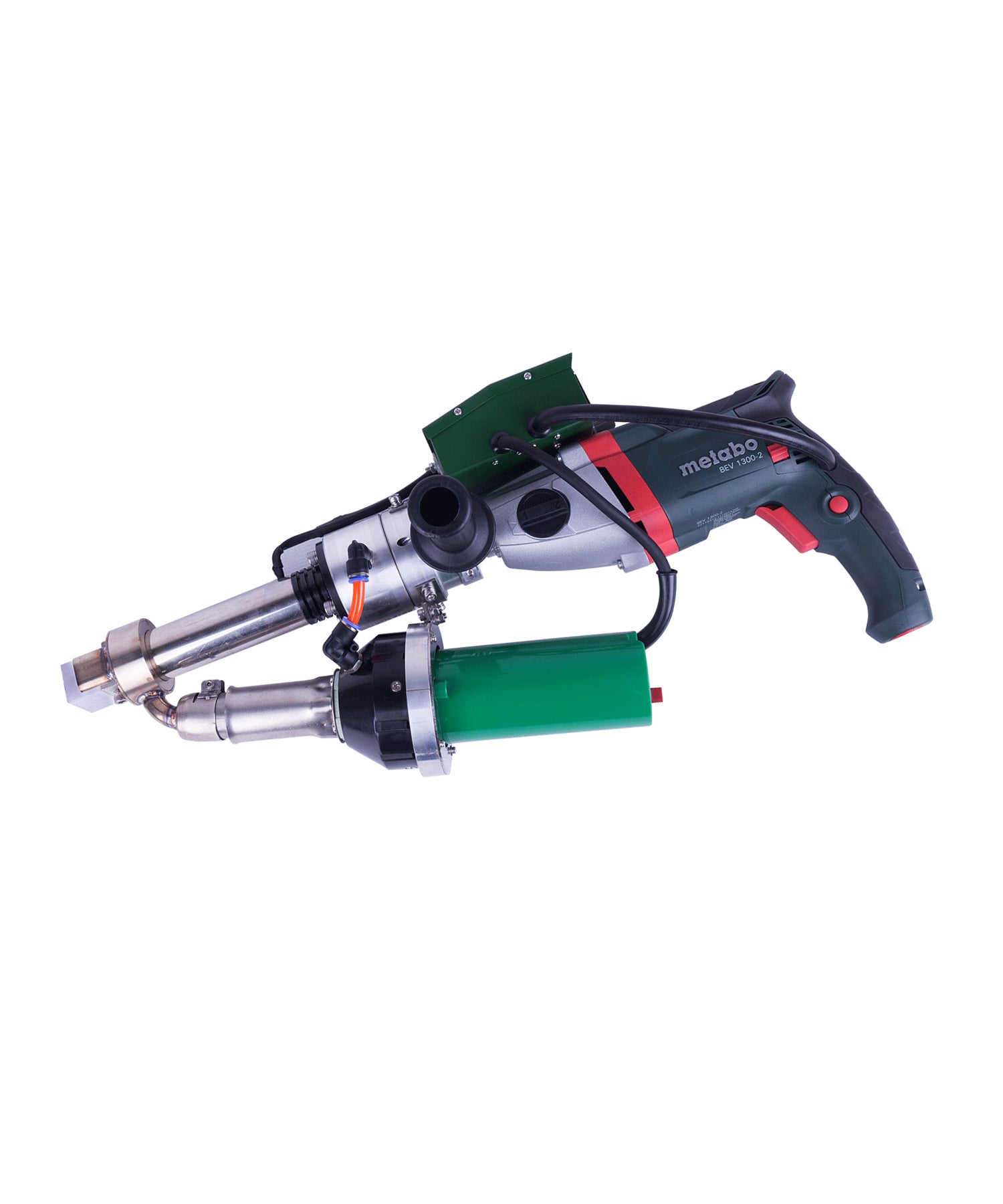
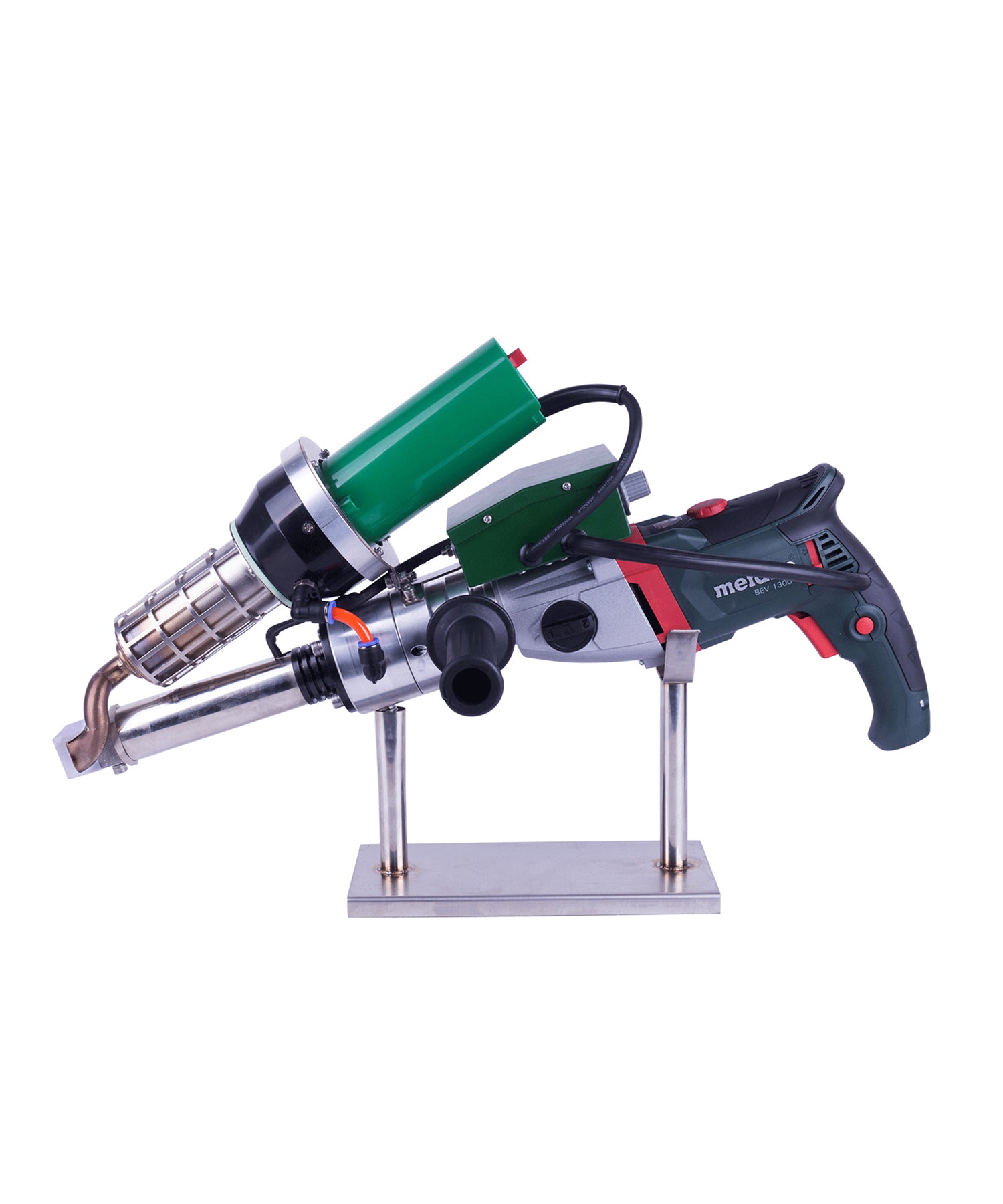
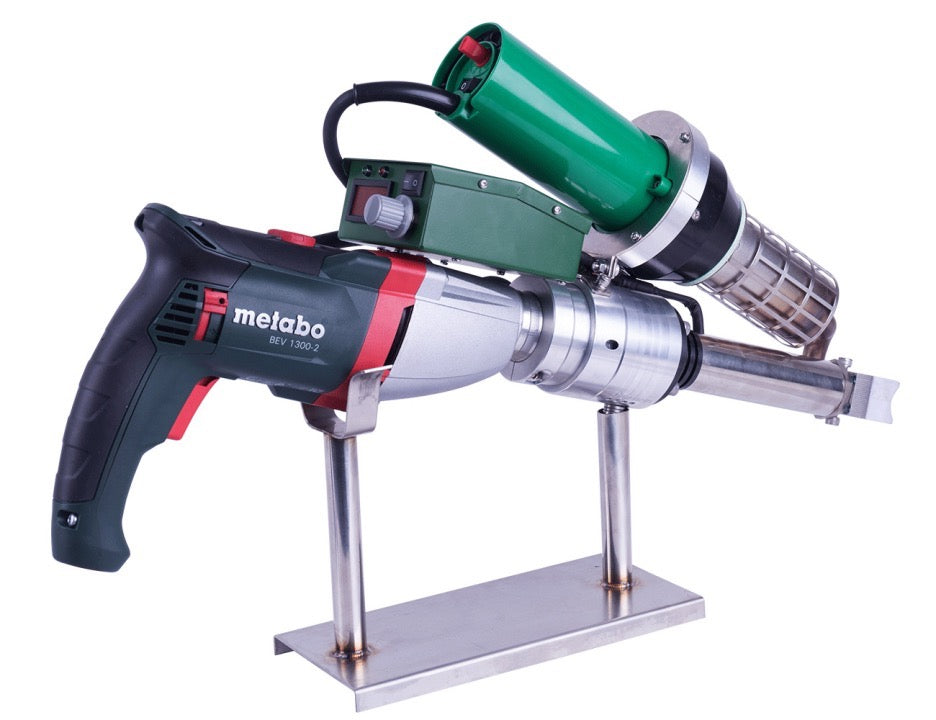
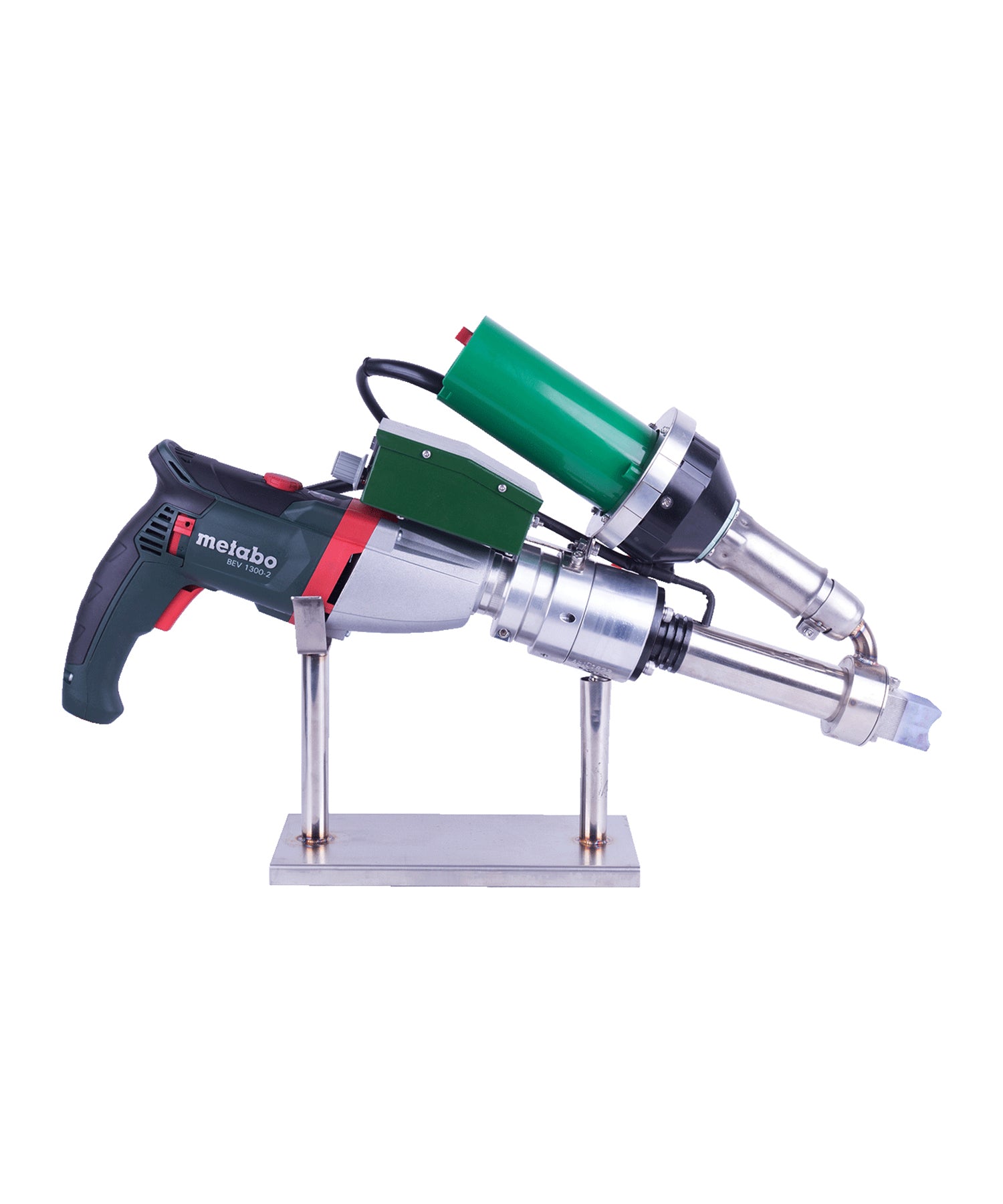
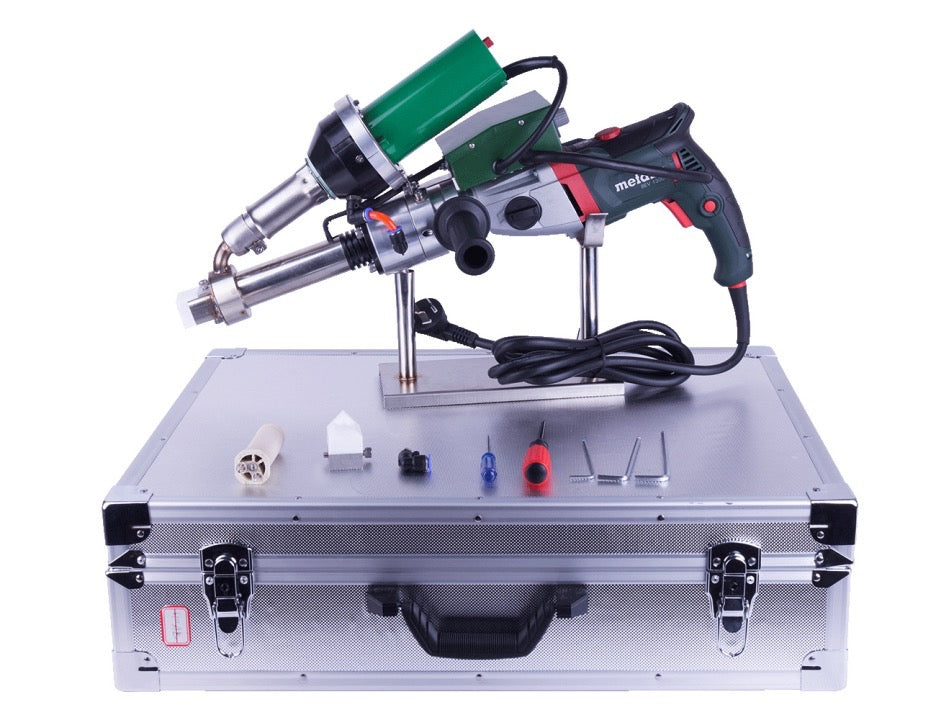
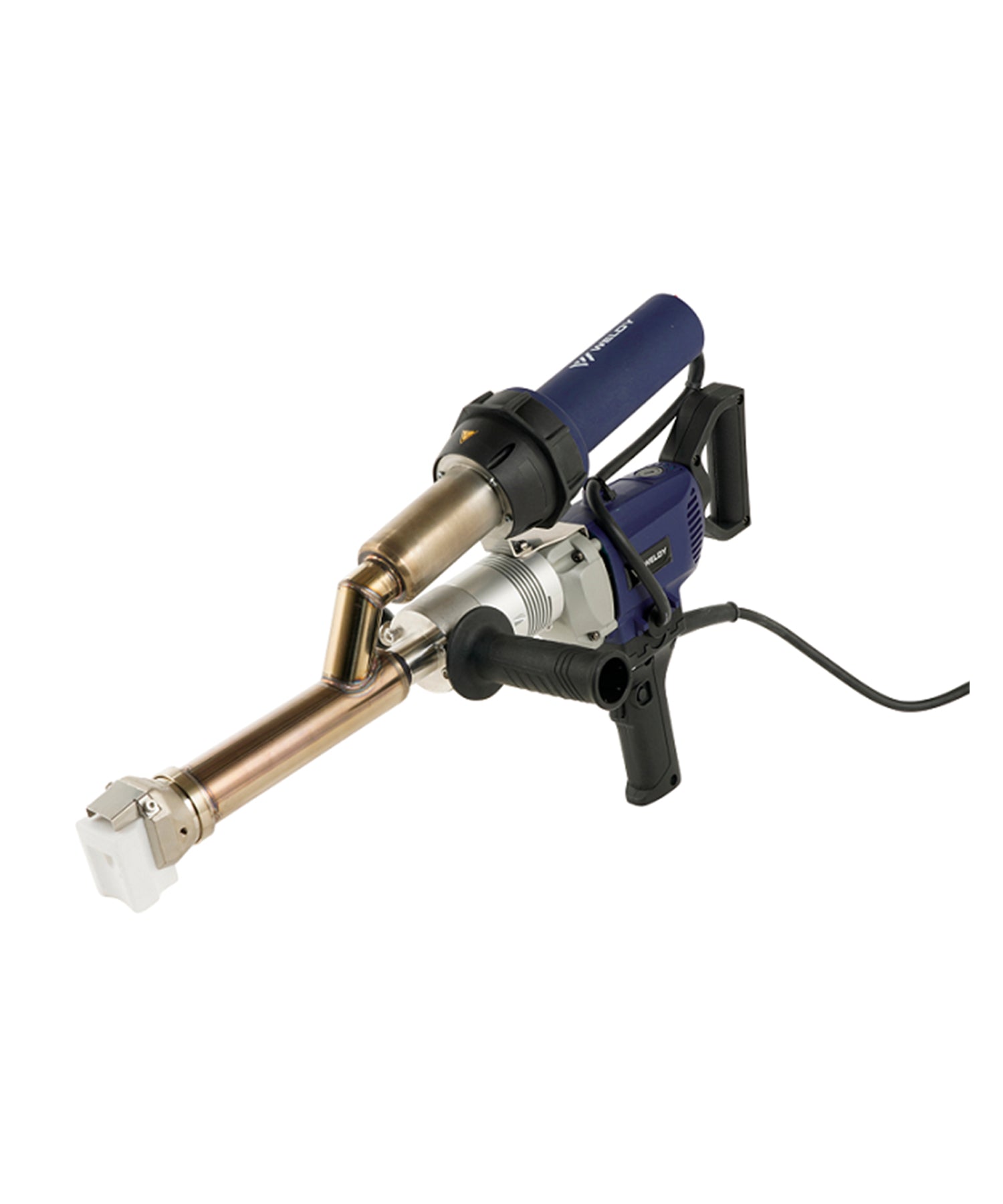
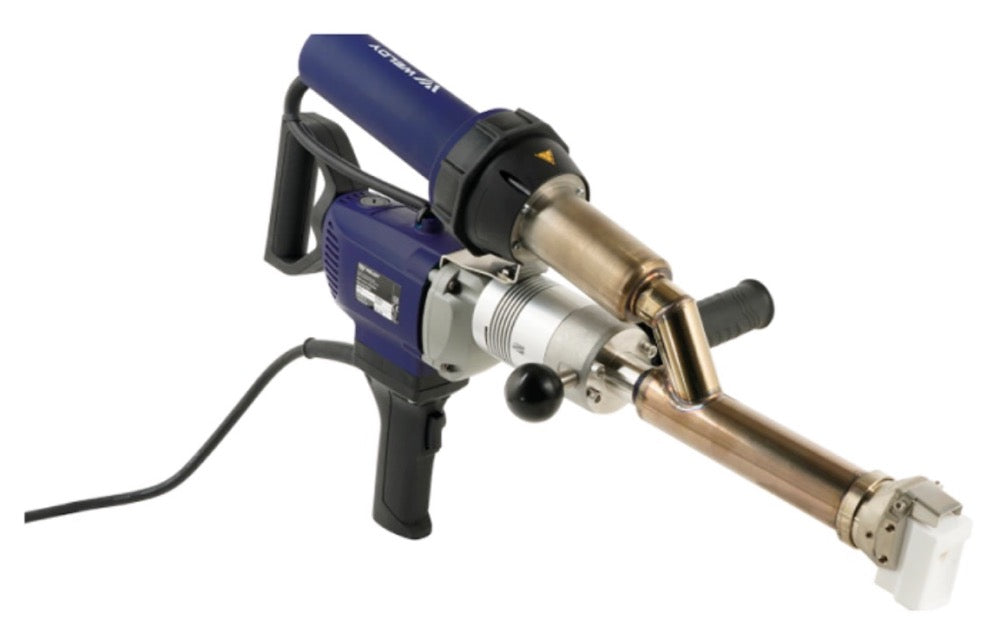
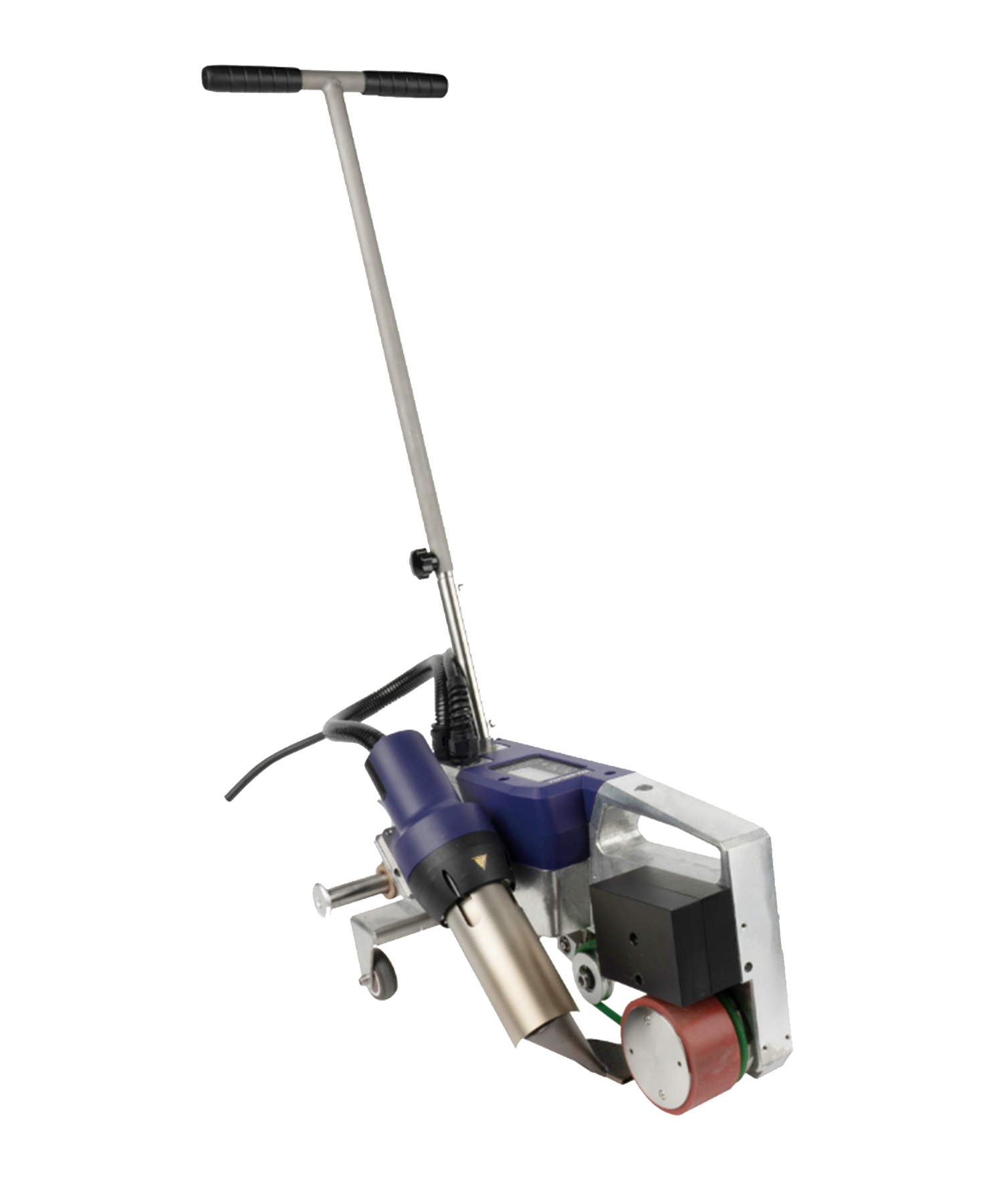
Hot air welding is one of the most widely used methods in roofing, particularly for PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and TPO (thermoplastic polyolefin) membranes. This technique uses a roof welding machine (hot air gun) to generate high-temperature airflow (typically 300-600°C), melting the membrane surface before applying pressure with a roller to fuse the materials seamlessly.
Construction Steps:
- Preparation: Clean the welding area to remove dust, oil, and moisture.
- Preheating: Use the hot air gun to evenly heat the overlapping edges (approx. 4-6 cm wide).
- Roller Bonding: Press the melted materials together with a roller for tight adhesion.
- Cooling & Inspection: After cooling, check the weld for bubbles or weak spots.
Advantages
- High-strength bonding: Molten welding ensures molecular fusion, stronger than adhesive bonding.
- Weather resistance: Suitable for extreme temperatures (-40°C to 80°C).
- Eco-friendly: No chemical solvents, reducing VOC emissions.
Disadvantages
- Skill-dependent: Improper temperature or pressure may cause weak welds or burn-through.
- Higher equipment cost: Professional welding machines are expensive, best for large-scale projects.
Applications
- Large commercial roofs (e.g., factories, shopping malls)
- Long-term waterproofing projects (e.g., underground garage decks)
Solvent Welding
Principle and Process
Solvent welding uses chemical solvents to soften the membrane surface, allowing molecular penetration. After evaporation, the materials bond firmly. This method is commonly used for PVC and some modified bitumen membranes, especially for complex shapes or small repairs.
Construction Steps:
- Surface Treatment: Sand and clean the welding area for better adhesion.
- Solvent Application: Brush the solvent (e.g., tetrahydrofuran, cyclohexanone) evenly.
- Bonding & Pressing: Press the materials together and hold until the solvent evaporates (~10-30 min).
- Curing & Inspection: Full strength is achieved after 24 hours.
Advantages
- No heavy equipment needed: Ideal for small-scale or repair work.
- High flexibility: Suitable for irregular areas (e.g., pipe penetrations, corners).
Disadvantages
- Toxic fumes: Solvents may release harmful gases, requiring ventilation and protective gear.
- Lower strength: Less resistant to long-term UV exposure or mechanical stress than hot air welding.
Applications
- Small roofs or localized repairs
- Complex detailing (e.g., skylights, drains)
Adhesive Bonding
Principle and Process
Though not true welding, adhesive bonding is often called "cold welding" due to its widespread use in roofing. It relies on polyurethane, acrylic, or epoxy adhesives to join membranes, making it suitable for EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) and other non-weldable materials.
Construction Steps:
- Surface Preparation: Ensure the substrate is dry and free of loose particles.
- Adhesive Application: Spread the adhesive (single or two-component) evenly with a trowel.
- Bonding & Rolling: Lay the membrane and use a roller to remove air bubbles.
- Curing: Typically takes 24-48 hours to reach full strength.
Advantages
- No heat damage risk: Safe for flammable or heat-sensitive materials.
- Easy installation: No specialized welders required, reducing labor costs.
Disadvantages
- Lower durability: UV exposure may degrade adhesive over time.
- Weather-sensitive: Humidity or low temperatures prolong curing time.
Applications
- EPDM rubber roofs
- Temporary waterproofing or renovation projects
Conclusion
The choice of roof welding technology directly impacts waterproofing performance and longevity. Hot air welding offers the best overall performance for high-standard projects, solvent welding is ideal for detail work, and adhesive bonding is necessary for EPDM and similar materials. Before construction, evaluate material properties, project scale, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal waterproofing.























Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.