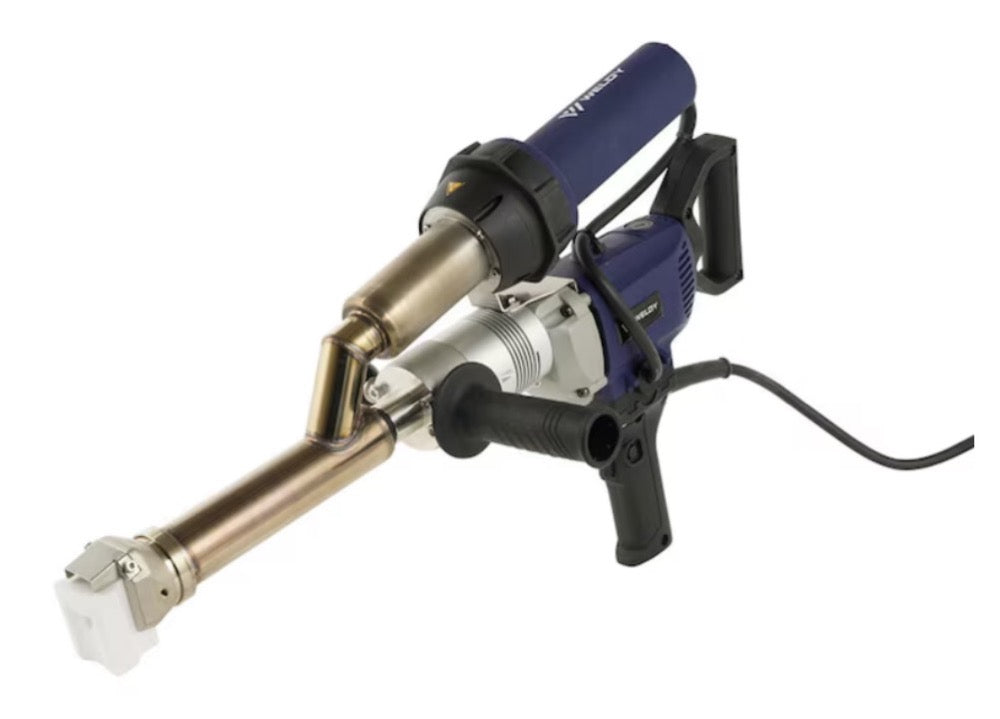
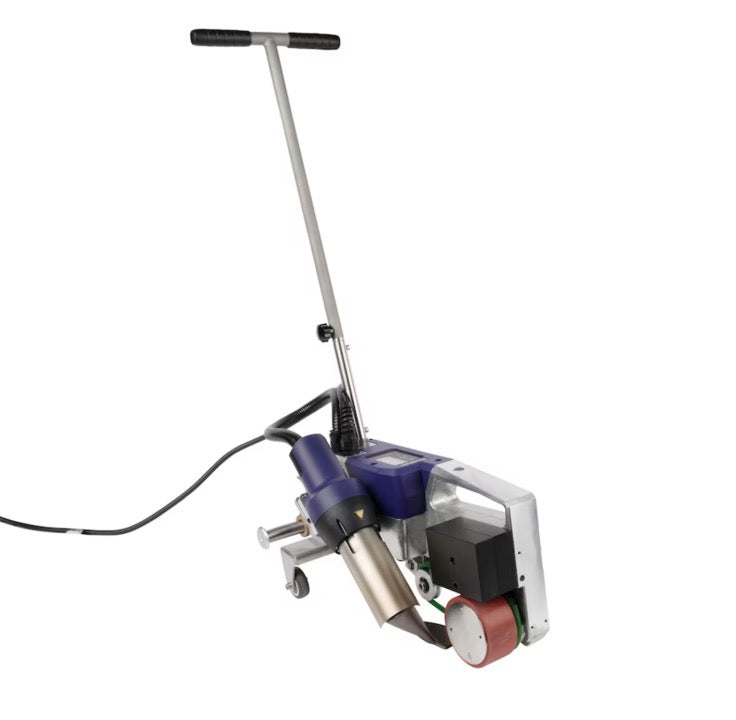
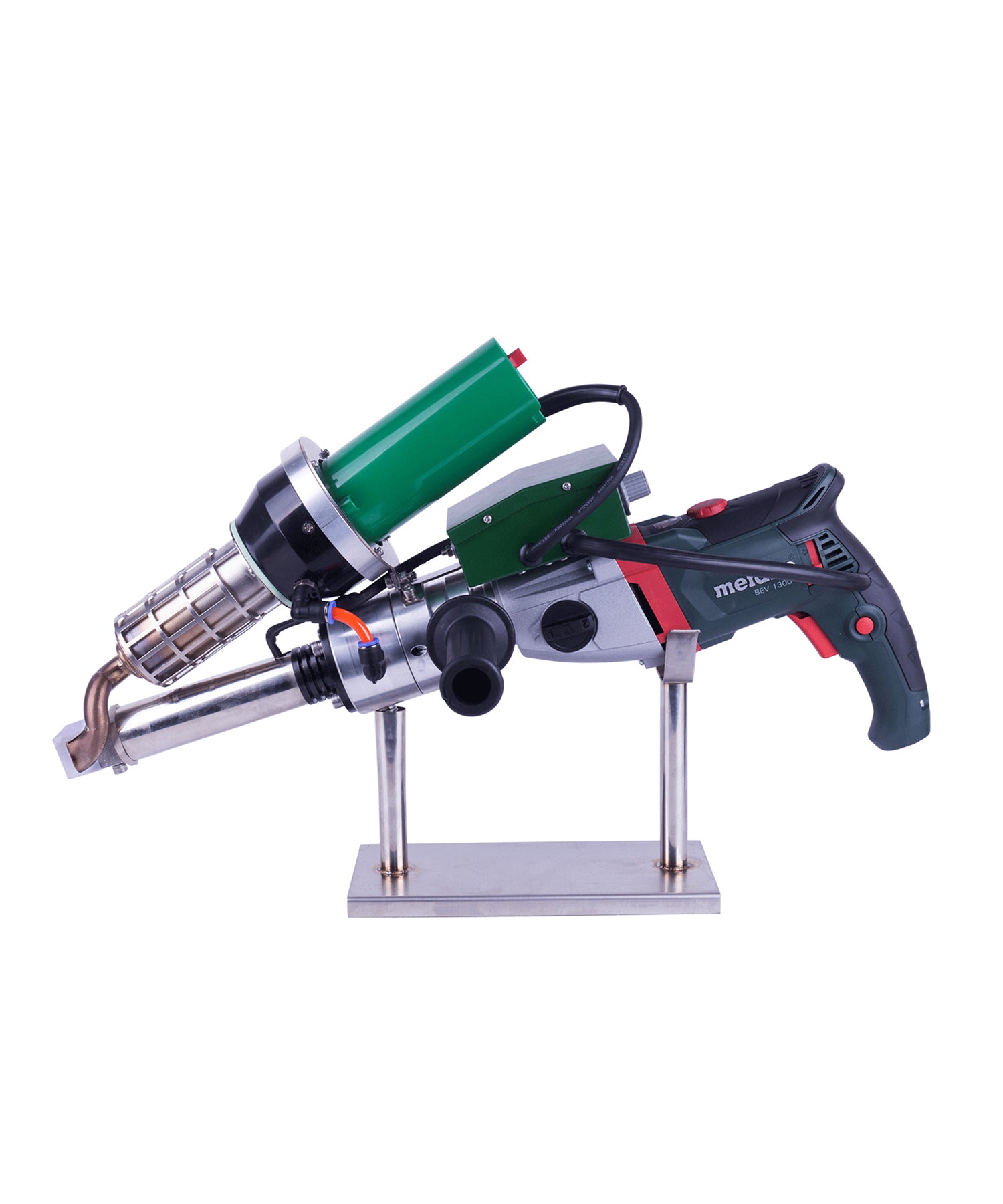
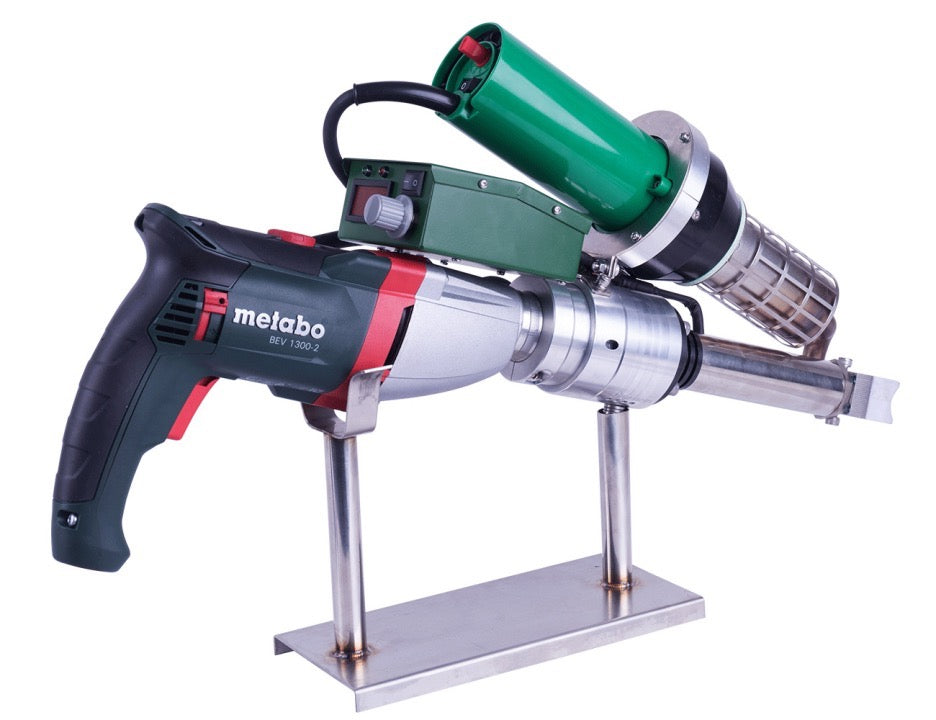
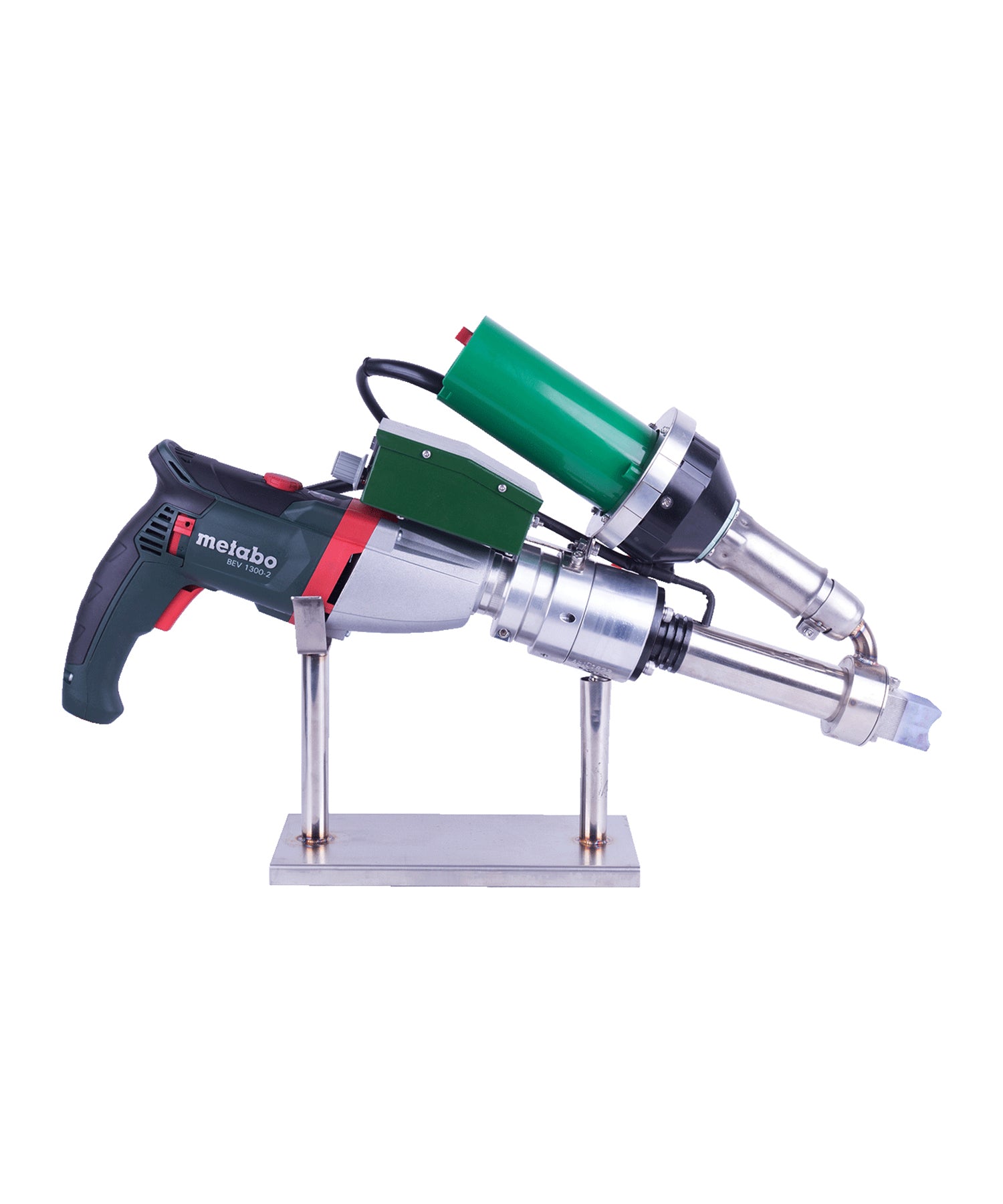
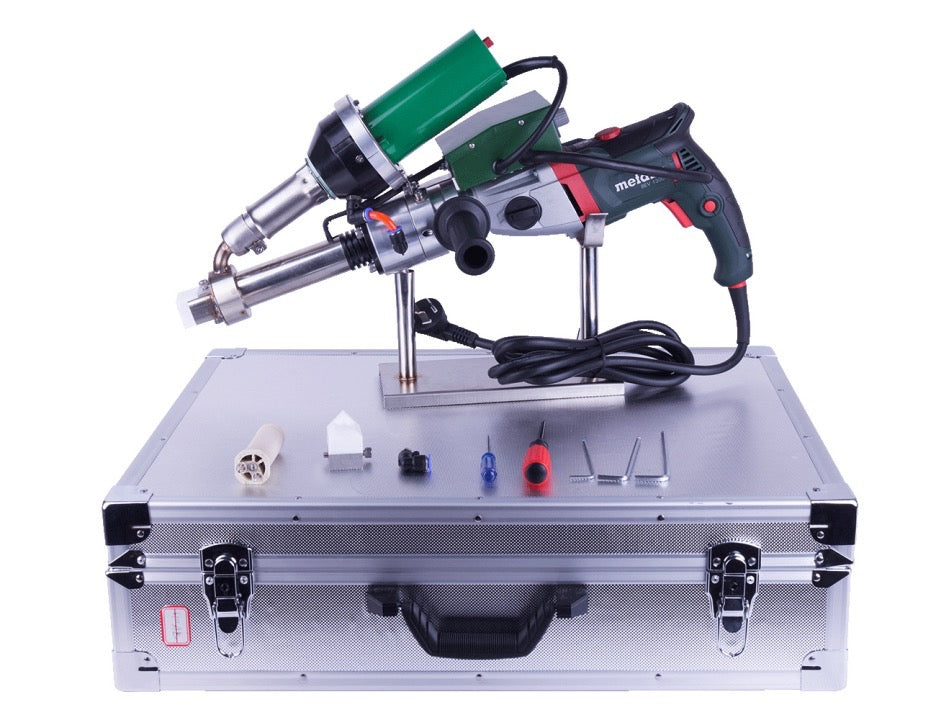
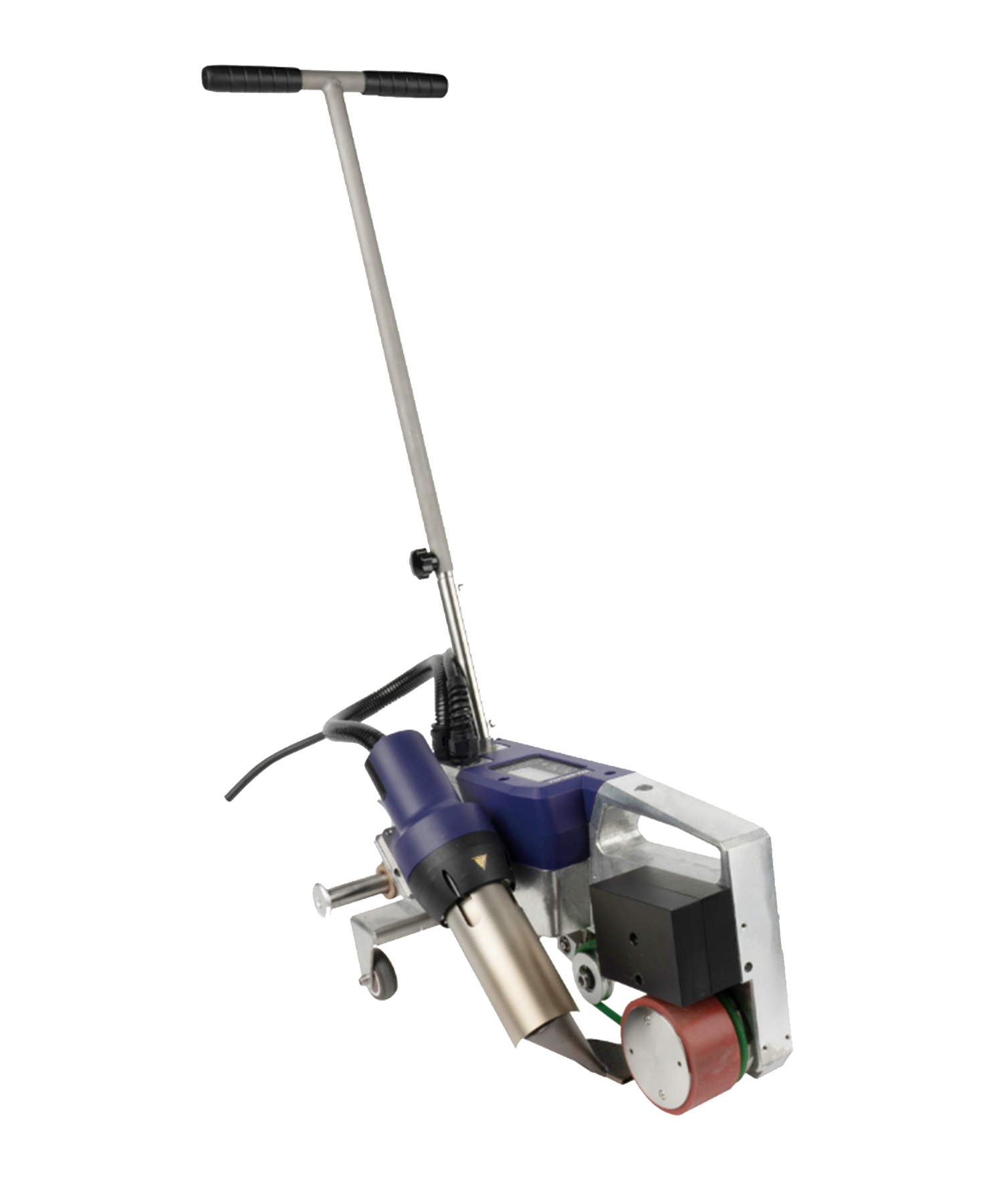
Extrusion welding machines are highly efficient and reliable tools used for welding thermoplastic materials, widely applied in industrial manufacturing, construction, environmental engineering, and specialized industries. The working principle involves heating a plastic welding rod until it melts and bonds with the base material, forming a high-strength, airtight weld seam. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the types of thermoplastics suitable for extrusion welding, key applications, technical advantages, and operational best practices, serving as a professional reference for related industries.
Types of Thermoplastics Suitable for Extrusion Welding
Extrusion welding machines can weld a variety of thermoplastics, each with unique physical and chemical properties suited for different industrial applications.
1. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
Properties:
- Excellent chemical resistance, high strength, and good flexibility.
- Low permeability, making it ideal for liquid or gas containment.
Primary Applications:
- Geomembrane Welding: Used in landfills, artificial lakes, and wastewater treatment ponds for anti-seepage engineering.
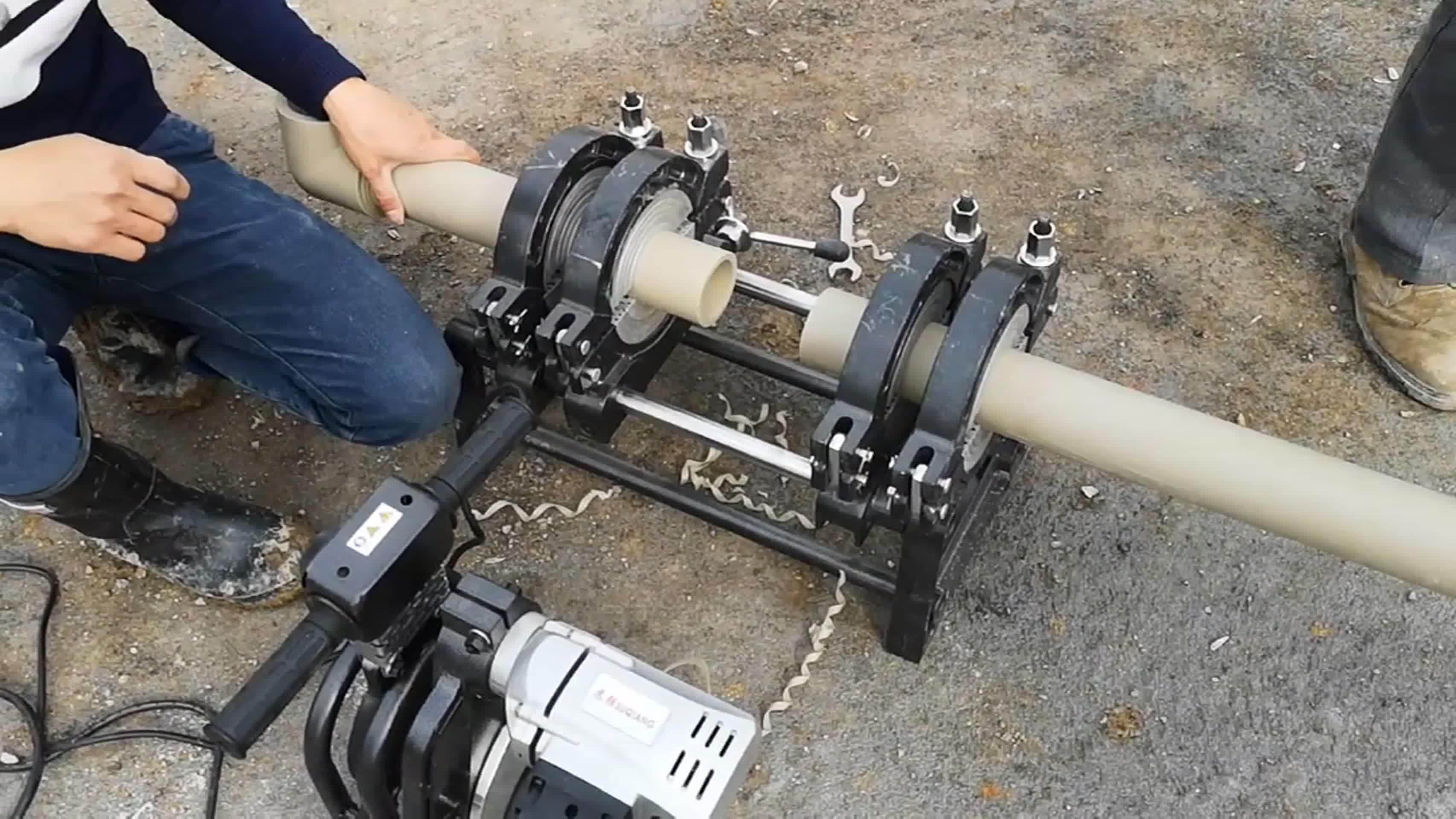
- Pipeline Connections: Welding HDPE pipes in chemical and municipal water supply/drainage systems.
- Storage Tank Fabrication: Seam welding for chemical tanks and acid/alkali-resistant containers.
Welding Guidelines:
- Optimal welding temperature: 250-300°C to ensure proper melting without degradation.
- Must use HDPE-specific welding rods for material compatibility.
2. PP (Polypropylene)
Properties:
- High heat resistance (up to 100°C+) and excellent acid/alkali resistance.
- Lightweight and easy to process but prone to brittleness at low temperatures.
Primary Applications:
- Chemical Equipment: Repairing tanks for aldehydes, acids, and alkalis.
- Automotive Industry: Seam welding for fuel tanks and ventilation ducts.
- Food Industry: Seamless joining of PP containers.
Welding Guidelines:
- Recommended welding temperature: 280-320°C due to its higher melting point.
- Surface must be cleaned before welding to avoid contamination affecting bond strength.
3. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Properties:
- Good mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and weather resistance.
- Available in flexible (plasticized) and rigid (unplasticized) forms, requiring slightly different welding techniques.
Primary Applications:
- Piping Systems: Butt welding for drainage and chemical pipelines.
- Floor Welding: Seamless joining of industrial PVC flooring.
- Waterproofing Membranes: Roofing and tunnel waterproofing layer welding.
Welding Guidelines:
- Rigid PVC welding temperature: 220-250°C; flexible PVC slightly lower (200-230°C).
- Avoid overheating to prevent hydrochloric acid (HCl) gas release.
4. PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride)
Properties:
- Exceptional chemical resistance, tolerating strong acids, alkalis, and organic solvents.
- High-temperature resistance (up to 150°C continuously), suitable for harsh industrial environments.
Primary Applications:
- Semiconductor Industry: Ultra-pure water pipelines and chemical delivery systems.
- Chemical Equipment: Corrosion-resistant lining for reactors and storage tanks.
- New Energy Sector: Bonding lithium battery separators and photovoltaic backsheets.
Welding Guidelines:
- Requires high-temperature welding (300-350°C) with PVDF-specific rods.
- Maintain a clean environment to avoid impurities affecting weld purity.
Technical Advantages of Extrusion Welding Machines
Compared to traditional hot-air guns or ultrasonic welding, extrusion welding offers:
- High-Strength Welds: Molecular-level bonding with weld strength exceeding 85% of the base material.
- Thick Material Compatibility: Can weld 0.5mm-15mm thick plastics, ideal for HDPE geomembranes (1.0-3.0mm).
- Superior Sealing: Bubble-free, gap-free seams for liquid/gas containment.
- Field Flexibility: Portable design suits on-site repairs (e.g., landfill liner fixes).
Operational Procedures and Key Considerations
1. Standard Welding Process
- Surface Prep: Clean with alcohol or specialized solvents to remove grease/oxides.
- Preheating: Set gun temperature based on material (e.g., ~260°C for HDPE).
- Welding: Feed the rod evenly for consistent melting.
- Post-Weld: Allow natural cooling; avoid mechanical stress.
2. Common Issues and Solutions
|
Issue |
Cause |
Solution |
|
Weld Cracking |
Low temperature or fast speed |
Increase heat, reduce speed |
|
Poor Adhesion |
Contamination or material mismatch |
Clean surface, switch rods |
|
Bubbles in Weld |
Moisture or overheating |
Pre-dry material, adjust temperature |
Industry Case Studies
- Environmental Engineering: A landfill used HDPE extrusion welding for 50,000㎡ geomembrane, achieving <0.01% leakage.
- Chemical Industry: PVDF-welded hydrochloric acid tanks showed zero leaks after 10 years.
- Construction: PVC floor welding enhanced durability by 50% with seamless joins.
Future Trends
- Smart Upgrades: Integrated temperature sensors and auto-speed adjustment for consistency.
- Eco-Friendly Tech: Low-energy, fume-free welding rods.
- New Material Adaptation: Machines optimized for advanced plastics like TPU and ECTFE.
Conclusion
Extrusion welding machines are indispensable for thermoplastic welding due to their material versatility, high-strength seams, and industrial adaptability. Proper parameter selection and standardized operations ensure optimal results. With advancements in smart and green technologies, their applications will continue expanding.























Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.